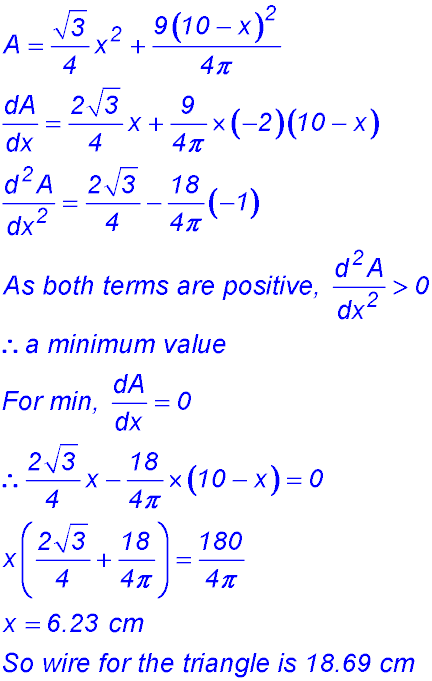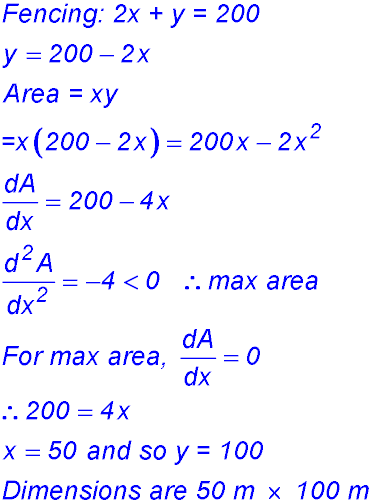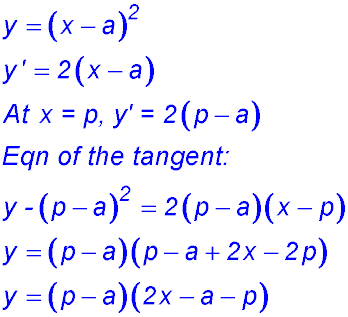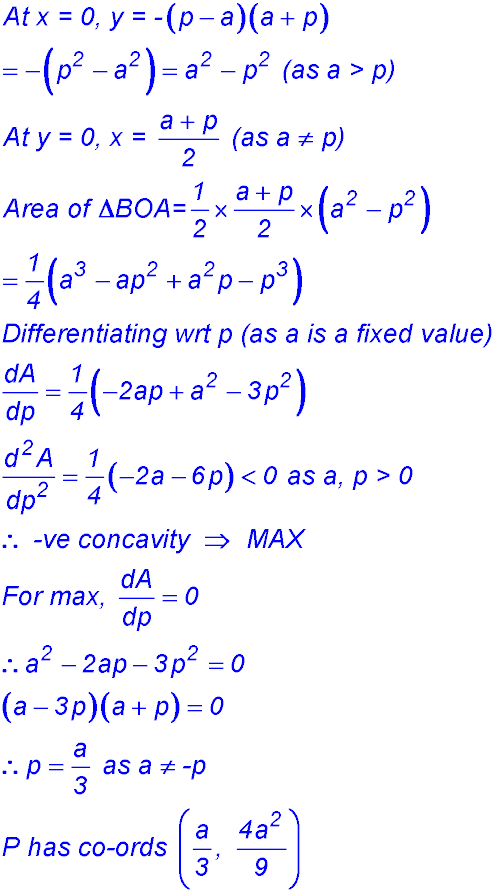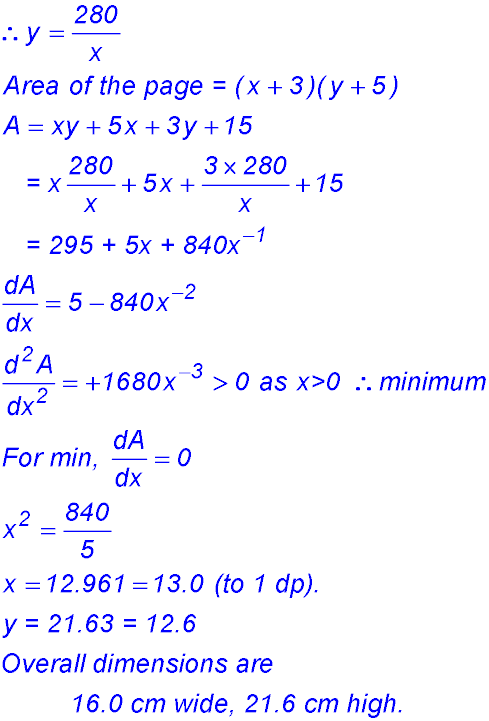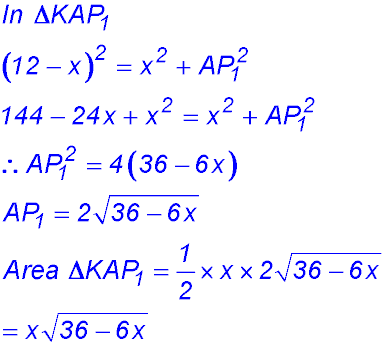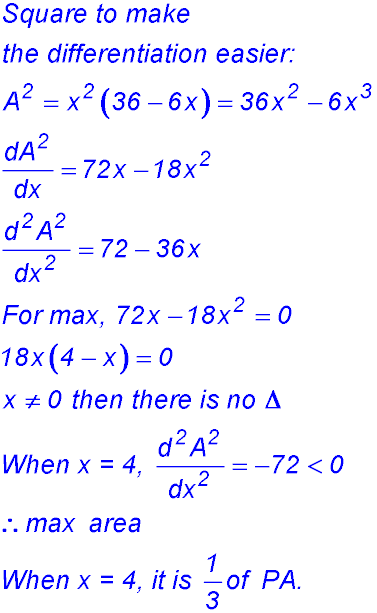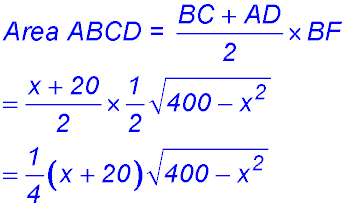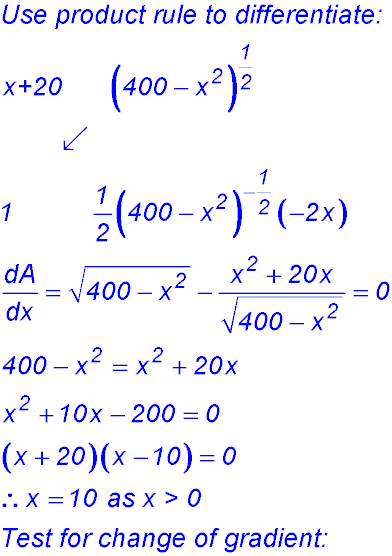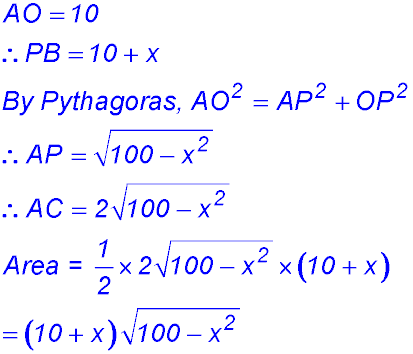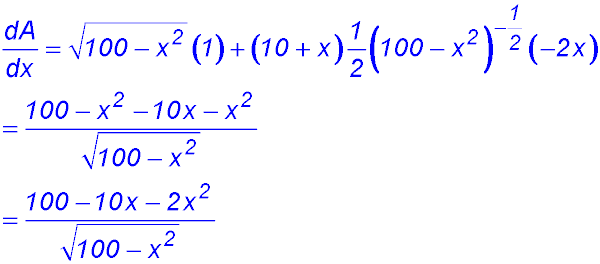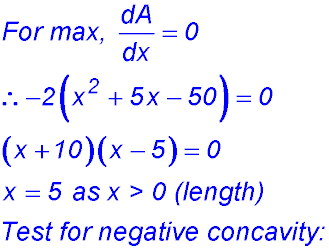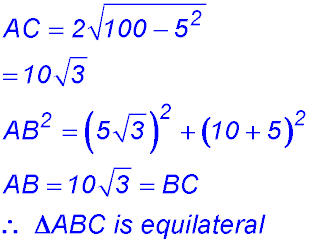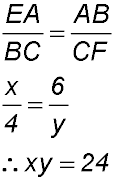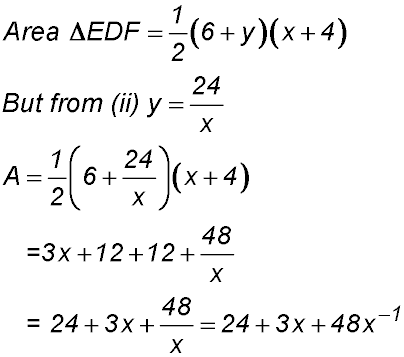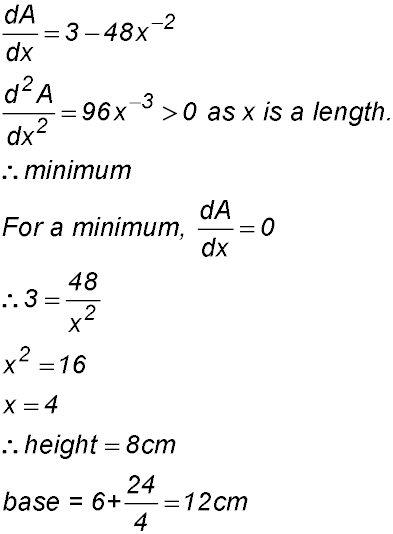Where the techniques of Maths
are explained in simple terms.
Calculus - Differentiation - Applied max/min questions.
Type 2: 2D shapes - Test Yourself 1 - Solutions.
- Algebra & Number
- Calculus
- Financial Maths
- Functions & Quadratics
- Geometry
- Measurement
- Networks & Graphs
- Probability & Statistics
- Trigonometry
- Maths & beyond
- Index
| Creating 2 shapes | 1. (i) 
(ii) |
||||||||
2. 
|
|||||||||
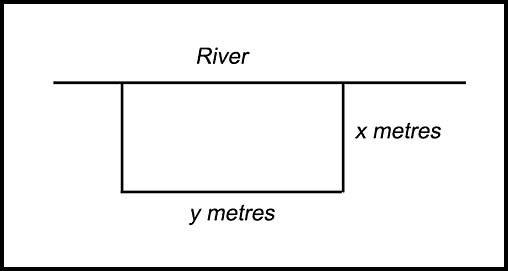
| Areas and paddocks. | 3. (i) (ii) |
||||||||
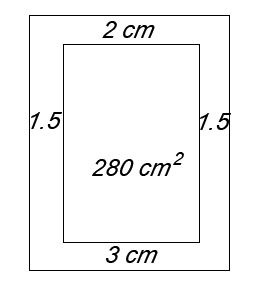
4. Let the dimensions of the printed area be x cm wide and y cm high. Hence area of printed material is A = xy = 280 cm2.
|
|||||||||
5. 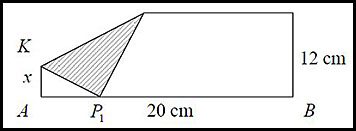
(i) PA was 12 cm long. After the fold, x cm (KA) remains vertical so the balance KP1 must be the difference - so (12 - x) cm. (ii) (iii) |
|||||||||
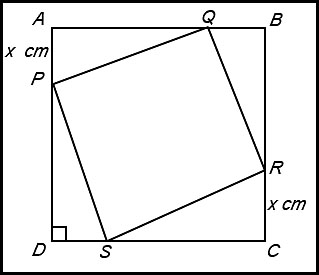
6. (i) PD = 10 - x = AQ = BR = SC. So we can apply Pythagoras' Theorem to calculate (say) PS. PS2 = x2 + (10-x)2. We could take the square root to calculate PS but, So the area of the square PQRS is A = x2 + (10-x)2
|
|||||||||
| Geometric shapes. | 7.
|
||||||||
8. (i) 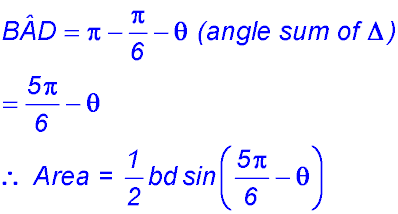
(ii) |
|||||||||
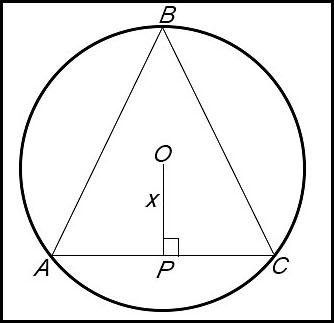
9. (i) 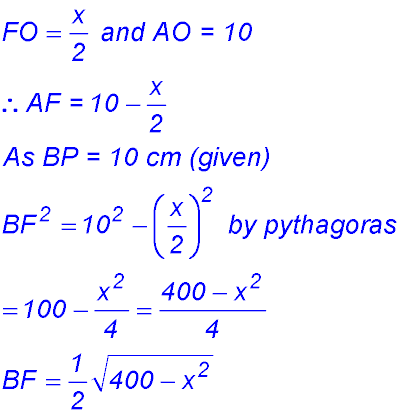
(ii) (iii)
So change of gradient around x = 10 from -ve to +ve - hence a maximum value for A. ∴ BC = 10 cm. |
|||||||||
10. (i) (ii) (iii)
Change of gradient -ve to +ve so a maximum value.
|
|||||||||
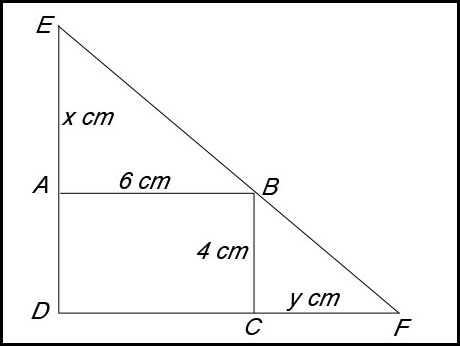
11. (i) ABCD is a rectangle and so AB//DCF and EAD//BC.
(ii) Ratioing corresponding sides in silimar triangles:
(iii) ED = x + 4 and DF = 6 + y
(iv) |
|||||||||
| Distance between 2 curves. |
12. (i) (ii) D = top curve - bottom curve.
(iii)
|
||||||||
| 13. |